Introduction
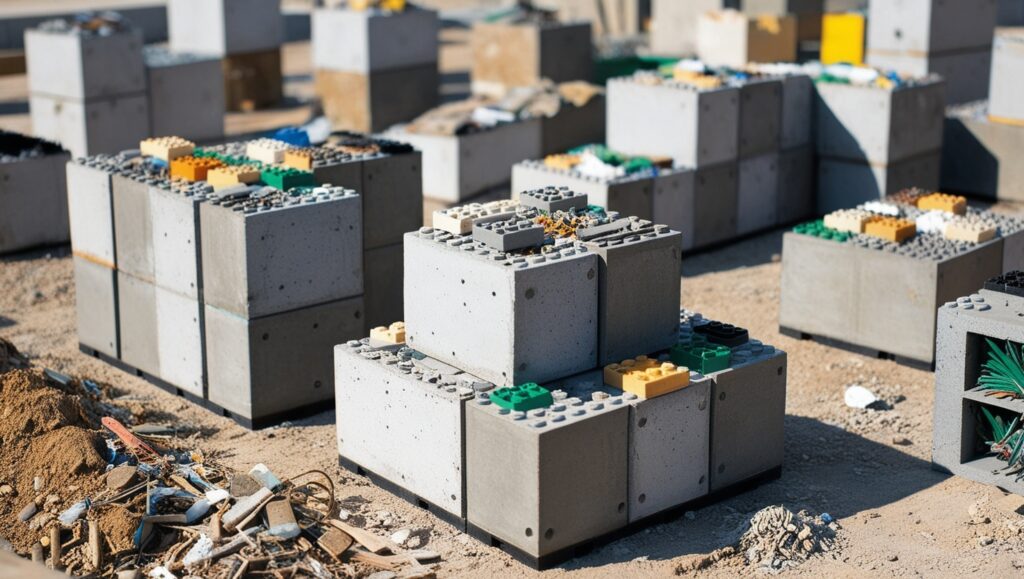
LEGO-like concrete blocks made from waste materials represent a significant innovation in sustainable construction, providing an efficient, cost-effective alternative to traditional building methods. These modular blocks, designed for easy assembly and disassembly, are primarily composed of recycled plastics, aggregates, and other construction debris, making them both eco-friendly and resource-efficient.
With a focus on reducing landfill waste and carbon emissions, these blocks align with the growing trend towards sustainability in the construction industry, addressing pressing challenges such as material shortages and escalating construction costs.
One of the key advantages of these interlocking blocks is their structural integrity and durability, which is enhanced by their unique design that eliminates the need for mortar. This not only speeds up construction time but also facilitates DIY projects, enabling homeowners and developers alike to engage in building their own structures with minimal professional assistance.
Notably, systems like Polycare leverage local waste materials, resulting in products that are up to five times stronger than traditional concrete while using significantly less material.
Despite their promise, the adoption of LEGO-like concrete blocks faces challenges, including regulatory hurdles and the need for standardized quality control. Additionally, initial investment costs and the complexities of integrating recycled materials into mainstream construction can deter widespread implementation.
Nevertheless, innovative applications in modular housing and urban development showcase the potential of these blocks to transform the construction landscape, making them a pivotal element in the pursuit of sustainable building practices and circular economies.
As the construction industry grapples with environmental and economic pressures, LEGO-like concrete blocks emerge as a viable solution that not only meets the demands for affordable housing but also contributes to a greener future. By promoting the use of recycled materials, these blocks represent a significant shift towards eco-conscious building methods that resonate with contemporary sustainability goals.
Background
Concrete Masonry Units (CMUs) emerged in the late 19th century, characterized by a variety of patented block designs and production methods. Despite their benefits, such as excellent fire resistance, sound insulation, and durability, the assembly of CMU walls has been deemed slow, tedious, and costly compared to alternative construction methods.
Recently, the rising costs of materials and labor shortages have led to a decline in the popularity of CMUs, prompting the development of innovative alternatives.
One notable innovation is the interlocking and stackable design of building blocks reminiscent of LEGO, which significantly simplifies the construction process. These blocks facilitate DIY construction, allowing homeowners to engage in building their own structures.
The Polycare block system exemplifies this shift; it consists of a mixture that is 90% natural sands and 10% liquid binder, forming a geopolymer concrete block that is five times stronger than traditional concrete while using 75% less material.
The introduction of other eco-friendly materials, such as hempcrete from Just-Biofiber, further illustrates the trend towards sustainability in building practices. Just-Biofiber’s blocks are made from a biocomposite frame cast with hempcrete, enabling the construction of tall walls while being lightweight and efficient for residential buildings.
Additionally, the utilization of recycled materials in building systems, like the ByBlock, has gained traction as a means to reduce environmental impact and promote sustainability within the construction industry.
As ecological concerns grow, interlocking concrete blocks have emerged as a viable solution, recognized for their durability, ease of assembly, and reduced ecological footprint. These materials are recyclable, reusable, and can be produced locally, which minimizes transportation costs and carbon emissions.
The construction industry’s increasing embrace of such systems reflects a broader shift towards sustainable building practices, responding to both economic and environmental challenges faced today.
Material Composition
The composition of LEGO-like concrete blocks, particularly those made from recycled materials, emphasizes sustainability and resource efficiency. The primary raw materials for these blocks often include a mixture of recycled plastics and aggregates, such as concrete and other construction and demolition (C&D) debris. C&D materials commonly utilized in such innovations include wood, metals, glass, and gypsum, as well as salvaged building components, all of which can be diverted from landfills and repurposed for new construction projects.
Recycled Plastics
The integration of recycled plastics into the manufacturing process is a significant aspect of these concrete blocks. These plastics are collected, sorted, cleaned, and processed into a usable form. The manufacturing process typically involves shredding the plastics, followed by melting and forming them into a paste-like consistency, which serves as the base material for the blocks.
In addition to recycled plastics, supplementary components such as colorants, UV inhibitors, and flame retardants may be added to enhance the durability, aesthetic appeal, and fire resistance of the final product.
Gypsum and Other C&D Materials
Gypsum, primarily derived from drywall, is another critical component in the composition of these blocks. Its recyclable nature allows it to be reprocessed into new drywall or utilized as a soil amendment, contributing to sustainable building practices. Other materials such as steel are often incorporated due to their high recyclability and strength, further promoting the use of sustainable materials in construction.
Benefits of Material Composition
The use of these varied materials not only reduces waste directed to landfills but also offers cost savings for builders and homeowners. By opting for blocks made from recycled materials, the construction industry is actively moving towards a circular economy, emphasizing reduced greenhouse gas emissions and conservation of natural resources.
Furthermore, the innovative design of these blocks—allowing for easy assembly and disassembly—aligns with modern building practices aimed at flexibility and sustainability in construction.
Design Features
Interlocking Mechanism
The innovative design of interlocking concrete blocks enables them to fit together without the need for mortar or cement. This unique interlocking mechanism utilizes protrusions and indentations, allowing each block to securely join with its neighbors, resulting in stable wall assemblies and enhanced structural integrity.
The lightweight nature of these blocks simplifies the assembly process, making them suitable for DIY projects and large-scale constructions alike.
Modular Configuration
The modular nature of these blocks facilitates various configurations and designs. Each block is designed to work within a standardized dimension, allowing for flexibility in layout while maintaining ease of assembly. As stated by a developer, the blocks can be arranged in increments, which helps maximize material efficiency and streamline the construction process.
This adaptability supports the creation of diverse structures, from retaining walls to industrial buildings, without sacrificing quality or stability.
Sustainability and Recyclability
Manufactured using recycled materials, these interlocking blocks represent a significant advancement in sustainable building practices. The emphasis on utilizing waste materials not only reduces environmental impact but also promotes a circular economy in construction.
Moreover, the standardization in design aids in effective recycling, ensuring that the materials can be repurposed after their initial use, thereby supporting zero-waste initiatives in the industry.
Educational Applications
Beyond their use in construction, interlocking blocks serve educational purposes as well. Their design enables hands-on learning experiences, where students can manipulate the blocks to understand mechanical physics concepts, as well as engage in 3D design projects. This feature makes them suitable for both kinaesthetic and visual learning styles, enhancing their appeal in educational settings.
Customization Options
The interlocking blocks are available in various shapes and sizes, allowing for customization in design. Some modern variants include blocks that resemble natural stones for aesthetic appeal, and soundproof variants that incorporate specialized materials for enhanced acoustic properties. This customization ensures that builders can meet specific functional and aesthetic requirements for any project.
Applications
Modular Housing Construction
The LEGO-like concrete blocks developed by Renco USA are particularly promising for modular housing construction. These blocks, made from recycled plastic and glass fibers mixed with resin and stone, allow for quick assembly and disassembly, addressing the urgent need for affordable housing in the U.S.
They can be combined with various roofing styles, enabling customizable design while reducing construction time significantly, with claims that homes can be completed within a week and with minimal waste.
Environmental Solutions
The Korean Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport has recognized the potential of these blocks in combating environmental issues within the construction sector. They have announced plans to utilize this modular system for constructing rental housing in the Seoul metropolitan area, suggesting that this technology can reduce construction costs and onsite operations, leading to faster project completion than traditional methods [15]. This aligns with broader trends aiming to enhance sustainability in building practices.
Innovative Applications in Urban Settings
In urban areas, these modular construction techniques can efficiently provide housing solutions amidst space constraints. For example, a project by Arquitectonica in the U.S. utilized the blocks to create an apartment complex comprising 96 units, showcasing their viability for large-scale applications. The design facilitates better space utilization and integrates modern aesthetics, which can attract residents seeking eco-friendly living options.
Construction Industry Transformation
The introduction of these blocks is part of a larger shift in the construction industry towards using sustainable materials and innovative building methods. As traditional construction methods struggle to keep pace with demand, particularly for affordable housing, solutions like the Renco blocks represent a paradigm shift that leverages waste materials to create functional living spaces, thus promoting a circular economy.
Integration with Modern Technologies
These blocks can also be complemented with emerging technologies in building management, such as smart facades that adapt to environmental conditions for optimal heating and cooling. This integration highlights the potential for creating energy-efficient and sustainable living environments, making the LEGO-like blocks a versatile option in modern construction practices.
Advantages
The use of LEGO-like concrete blocks made from waste materials offers several significant advantages in modern construction, contributing to sustainability and efficiency.
Environmental Benefits
Eco-friendliness and Sustainability
These innovative blocks are celebrated for their eco-friendly properties, as they often incorporate recycled materials, significantly reducing the environmental impact of brick production. The reduced use of cement in their composition leads to lower carbon emissions during manufacturing, promoting a greener construction process. Additionally, by conserving natural resources and minimizing landfill waste, the adoption of these blocks aids in the conservation of finite resources like aggregates, timber, and minerals.
Energy Savings
The energy required for extracting and processing raw materials is significantly reduced when using recycled blocks. This decrease in energy consumption not only lessens the overall carbon footprint of construction projects but also promotes a more sustainable building practice.
Economic Advantages
Cost Efficiency
Using recycled materials often proves to be more cost-effective than utilizing virgin resources. This affordability allows builders and developers to save money while still contributing to sustainable practices. Moreover, the growing demand for eco-friendly building solutions creates new markets and opportunities for innovative companies in the construction sector, further enhancing economic viability.
Structural Benefits
Strength and Durability
LEGO-like concrete blocks are designed to interlock, which provides enhanced structural integrity and durability. This interlocking mechanism ensures excellent load-bearing capacity, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from residential buildings to commercial structures. Their robust composition guarantees longevity, making them a reliable choice for builders and architects alike.
Ease of Assembly and Disassembly
One of the standout features of these blocks is their ease of assembly and disassembly. This modular approach allows for quicker construction times, reduced labor costs, and the ability to adapt structures as needed, ultimately leading to more flexible and efficient building processes.
Challenges
Technical Challenges
While the use of innovative, modular construction techniques such as those employed by Block Solutions offers many advantages, there are several technical challenges that must be addressed. One significant issue is the design and engineering of stackable building blocks, which may seem straightforward but requires extensive testing and optimization for structural integrity and airtightness. The development of these blocks has involved the use of prototypes and parametric software, in addition to collaborations with expert consultants to ensure that the system is robust and reliable.
Regulatory and Certification Challenges
The regulatory landscape poses another layer of complexity for the use of recycled materials in construction. Currently, there is a lack of national and international standards governing the quality and safety of modular construction components. This absence of standardization leads to inconsistent quality control and can complicate the certification processes necessary for mass-market acceptance. Ensuring compliance with local building codes and obtaining necessary certifications can also incur significant costs, which may deter some potential projects from using these innovative materials.
Economic Considerations
Economically, while the long-term benefits of using recycled materials are evident, initial costs and financial implications can pose challenges. A thorough cost-benefit analysis is essential for project feasibility, especially when dealing with innovative materials that may require higher upfront investments compared to traditional methods. Balancing these costs against the potential for sustainability and reduced environmental impact is critical for the widespread adoption of such construction practices.
On-Site Segregation and Waste Management
Implementing effective on-site waste segregation and management is vital for maximizing the benefits of using recycled materials. This requires proper training for construction workers and robust policing of job sites to prevent contamination of recyclable materials. Without efficient waste management practices, the advantages of using eco-friendly materials could be undermined, affecting both the project’s sustainability goals and its economic viability.
Case Studies
Polycare Construction System
The Polycare Construction System exemplifies the practical application of innovative building techniques utilizing sustainable materials. This modular approach emphasizes the use of locally sourced waste materials, enhancing both environmental sustainability and economic viability. The system enables easy assembly and disassembly of structures, thus supporting circular construction practices.
Materials
The Polycare system incorporates waste products in its composite materials, significantly reducing the environmental impact associated with traditional construction methods. Notably, the use of recycled and locally produced materials aligns with sustainability objectives by minimizing the carbon footprint of construction processes.
Design
The design of the Polycare structures prioritizes modularity, allowing for flexibility in construction and adaptation over time. This modularity not only facilitates efficient assembly but also promotes the reuse of materials at the end of a building’s life cycle, thus contributing to the circular economy.
Manufacturing and Assembly
Polycare’s manufacturing processes are streamlined to optimize resource efficiency. The construction method allows for rapid assembly on-site, reducing labor costs and time while maintaining high standards of quality and safety. Additionally, the approach minimizes waste generated during the construction phase, thereby enhancing overall sustainability.
Future Improvements
Ongoing research into the Polycare Construction System aims to further enhance its sustainability performance by integrating advanced technologies and innovative practices. Future improvements may focus on optimizing material composition, increasing the energy efficiency of production, and enhancing the design for disassembly features, thereby ensuring that the system remains at the forefront of sustainable building practices.
BIM-Based Disassembly Models
Another noteworthy case study involves the development of Building Information Modeling (BIM)-based disassembly models that support the reuse of building components. This framework allows stakeholders to visualize the disassembly process and evaluate the potential for recycling materials post-demolition.
By leveraging advanced modeling techniques, this approach not only improves resource efficiency but also fosters a culture of sustainability within the construction sector.
These case studies underscore the potential for innovative building practices that not only meet current construction demands but also pave the way for a sustainable future in the industry.
Future Prospects
The future of construction is increasingly leaning towards innovative solutions that integrate recycled materials, particularly in the context of addressing housing shortages and sustainability concerns. A notable trend involves the use of LEGO-like blocks made from recycled plastic and glass fibers, which are blended with resin and stone. This method offers a unique alternative to traditional materials such as wood and concrete, promising both affordability and efficiency in building practices.
Emerging Trends
Emerging technologies are enhancing the efficiency of recycling processes, enabling more thorough extraction of value from waste materials. Companies like Renco USA and Block Solutions are pioneering these advancements by creating building blocks that are not only cost-effective but also environmentally friendly, tackling the dual issues of affordable housing and plastic pollution simultaneously.
Furthermore, research into biodegradable materials is expanding, opening avenues for construction practices that significantly reduce long-term waste.
Integration with Sustainability Goals
The incorporation of recycled materials into construction aligns closely with global sustainability goals. For instance, integrating materials such as upcycled gypsum and steel can yield high-quality building components that are both durable and eco-friendly. These materials not only conserve landfill space but also reduce the extraction of natural resources.
Furthermore, innovation in building designs, including color-coded plans akin to those used in LEGO constructions, could streamline assembly processes and promote flexibility in building strategies.
Best Practices for Future Implementation
To maximize the potential of recycled construction materials, several best practices are recommended. Early planning and strong supplier relationships are crucial for ensuring a consistent supply of quality materials. Additionally, education and training for construction teams on the benefits and handling of these materials will play a significant role in their successful implementation.
As the construction industry adapts to these changes, the collective efforts of architects, contractors, and suppliers will be pivotal in driving sustainable practices forward. As we look ahead, the construction industry stands at a pivotal moment where the fusion of creativity, collaboration, and commitment to sustainability could lead to a greener future. By embracing recycled materials and innovative building techniques, we can address pressing challenges while creating a more sustainable world.



