Introduction to Suspension System in Automobile
The Automobile suspension system is a crucial component of any automobile, playing a vital role in ensuring a smooth, safe, and comfortable ride. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of automobile suspension systems, exploring their functions, types, components, and impact on vehicle performance. Whether you’re a car enthusiast, a student of automotive engineering, or simply a curious driver, this article will provide you with a deeper understanding of how suspension systems contribute to the overall driving experience.
For several years vehicle dynamics engineers have struggled to accomplish a suspension system by compromising between vehicle handling, ride comfort and stability. The outcomes of this are vibrant in the vehicles we see today. In common, at one extreme are large sedan and luxury cars with excellent ride qualities but only satisfactory handling behavior. On the last end of the spectrum are sports cars with very good handling but very firm ride quality. In between is any number of variations dictated by the vehicle manufacturer and target customer needs.
Every automotive suspension has two objectives: passenger comfort and vehicle control. Comfort is delivered by isolating the vehicle’s passengers from road disturbances like bumps or holes. Control is attained by maintaining the car body from rolling and pitching extremely and maintaining good contact stuck between the tire and the road. By and large, today’s vehicle suspensions use hydraulic dampers and springs that are charged with the tasks of absorbing bumps, decreasing the car’s body motions during accelerating, braking and turning and keeping the tires in contact with the road surface.
History of suspension systems
1903 – Mors from Germany fixed a car using shock absorbers.
1920 – Leyland used torsion bars in their suspension system.
1922 – Unitary constructions and independent front suspension were initiated on the Lancia Lambda.
1932 – By this year ,the independent front suspension became common in standard cars.
1948 – Triumph Mayflower presented the combined coil spring/damper unit.
1950 – Ford implemented the McPherson strut independent front suspension on MK 1 consul.
1959 – Usage of independent rubber suspension started.
1962 – Introduction of the hydrostatic suspension.
Why do vehicles have suspension system?
The purpose of a suspension system is to isolate the body and its residents from the irregularities of the road surface. In an ideal world the body should ride level and lacking vertical motion however bumpy the road surface. Another significant feature of suspension is that it should retain the tires on the ground all the time. If there were not at all suspension the tires would incline to lift off the ground every time they passed over a bump at the same time, the shock as the wheels left the ground’ and then came down another time, would be transferred precise to the passengers.

What does a suspension system do?
Preferably the suspension should allow the wheels to move up and down so that they follow the undulations in the road during the body rides level. The first necessity therefore is that the wheels should be capable of moving vertically relative to the body. All suspension has this wheel travel, which must be housed by some means.
Functions of suspension system
The vehicle suspension system is mainly responsible for driving comfort and safety as the suspension carries the vehicle body and transmits all forces between the body and the road. In order to completely influence these properties, semi-active and active components are introduced. These aid the suspension system to adapt to various driving conditions.
By addition of a variable damper and spring, driving comfort and safety are considerably improved related to suspension setups with fixed properties. To prevent the road shocks from existence transmitted to the vehicle frame.To preserve the stability of the vehicle in pitching or rolling.To maintain the occupants from road shocks.To provide good road holding while driving, cornering and braking.
Understanding the Importance of Suspension Systems
Suspension systems serve multiple critical functions in a vehicle:
- Ride Comfort: By absorbing shocks and vibrations from road irregularities, suspension systems ensure a smooth and comfortable ride for passengers.
- Handling and Stability: Proper suspension helps maintain optimal tire contact with the road surface, enhancing vehicle control and stability during cornering, acceleration, and braking.
- Load Management: Suspension systems support the vehicle’s weight and help distribute loads evenly, improving overall balance and performance.
- Component Protection: By reducing the impact of road shocks, suspension systems protect other vehicle components from excessive wear and damage.
Broad Classification of suspension system
Suspension systems can be generally classified into two subgroups: dependent and independent. These terms denote to the ability of opposite wheels to move independently of each other. A dependent suspension usually has a beam or live axle that holds wheels parallel to each other and perpendicular to the axle. When the camber of one wheel differs the camber of the opposite wheel changes in the same way (by convention on one side this is a positive change in camber and on the other side this a negative change).
An independent suspension permits wheels to rise and fall on their own without disturbing the opposite wheel. Suspensions with other devices like sway bars that link the wheels in some way are still classed as independent. A third type is a semi–dependent suspension. In this type, the motion of one wheel does disturb the position of the other but they are not firmly attached to each other. A twist beam rear suspension is such a kind of system.
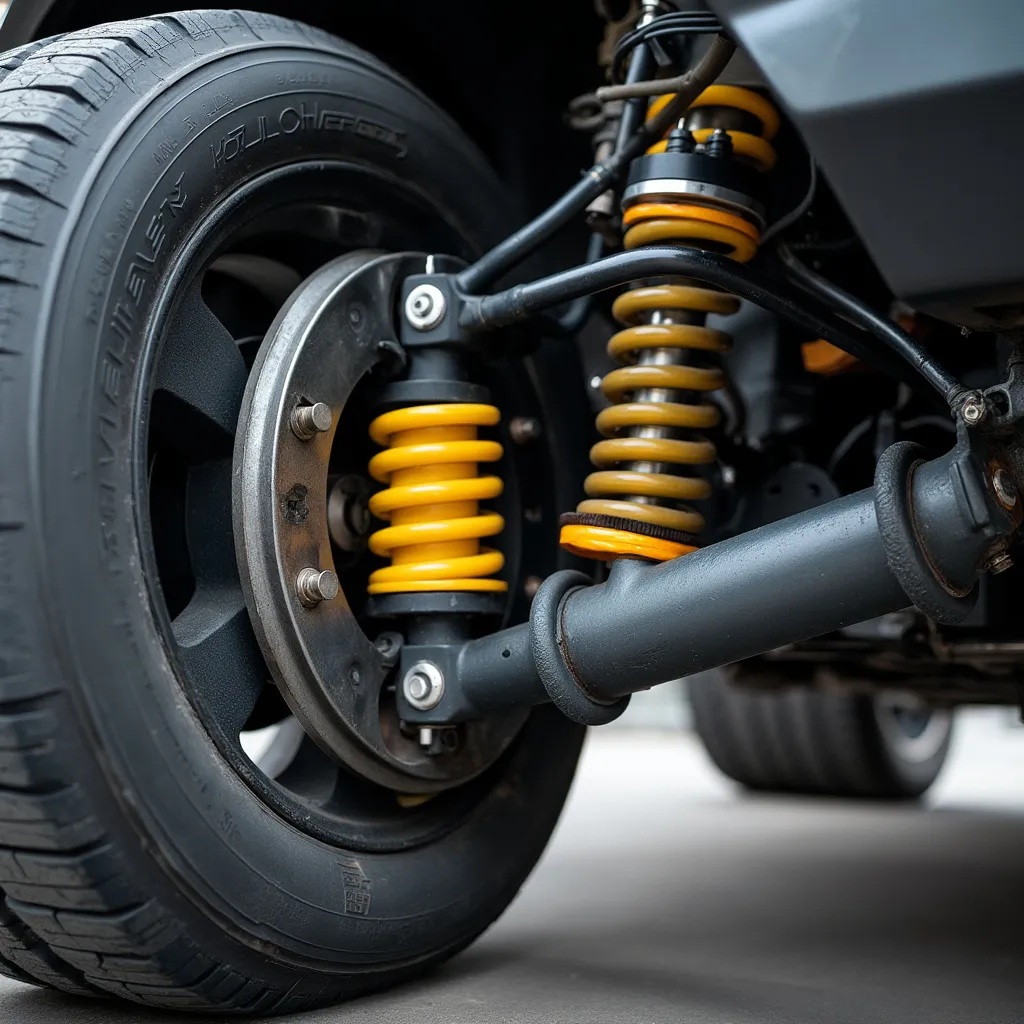

Types of Suspension Systems
There are several types of suspension systems used in modern automobiles, each with its own advantages and applications:
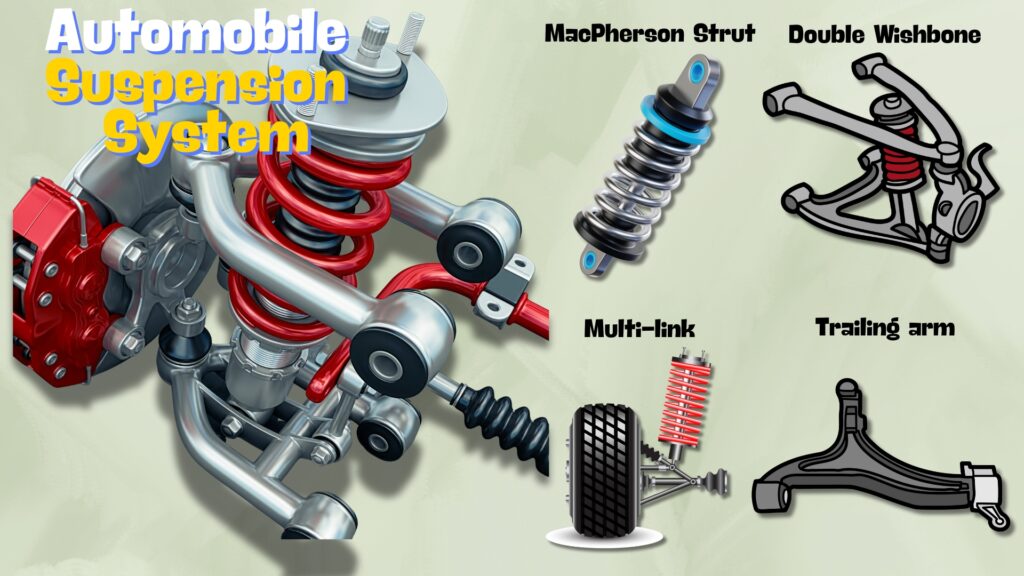
1. Independent Suspension
Independent suspension allows each wheel to move vertically without affecting the others. This system provides superior ride comfort and handling, especially on uneven surfaces.
Types of independent suspension include:
- MacPherson Strut
- Double Wishbone
- Multi-link
- Trailing Arm
2. Dependent Suspension
In a dependent suspension system, the movement of one wheel affects the other wheel on the same axle. While generally simpler and more robust, this system is less common in modern passenger vehicles due to its inferior ride quality compared to independent systems.
Types of dependent suspension include:
- Solid Axle
- Beam Axle
3. Semi-Independent Suspension
This system combines elements of both independent and dependent suspensions, offering a balance between performance and cost-effectiveness.
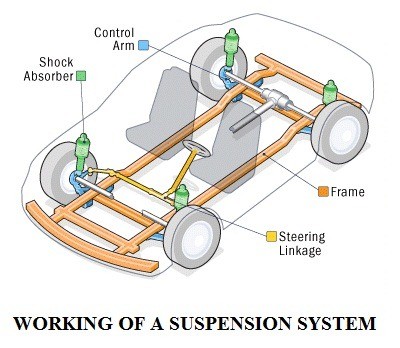
Key Components of Suspension Systems
Understanding the various components that make up a suspension system is crucial for grasping its overall function:
- Springs: These components support the vehicle’s weight and absorb road shocks. Common types include:
- Coil springs
- Leaf springs
- Torsion bars
- Air springs
- Shock Absorbers: Also known as dampers, these components control the spring’s oscillation, preventing excessive bouncing and ensuring a smooth ride.
- Struts: Combining the functions of a shock absorber and a structural support component, struts are commonly used in modern vehicles, especially in MacPherson strut suspensions.
- Control Arms: These components connect the wheel hub to the vehicle’s frame or body, allowing for vertical movement while maintaining proper wheel alignment.
- Ball Joints: These flexible pivot points allow for steering and suspension movement while maintaining proper wheel alignment.
- Bushings: Made of rubber or polyurethane, bushings reduce friction between metal components and help isolate vibrations.
- Sway Bars: Also known as anti-roll bars, these components reduce body roll during cornering by connecting the left and right sides of the suspension.
Factors Influencing Suspension Design
Several factors influence the design and selection of suspension systems for different vehicles:
- Vehicle Type and Purpose: Sports cars require different suspension characteristics compared to off-road vehicles or luxury sedans.
- Weight Distribution: The distribution of weight between the front and rear axles affects suspension design and tuning.
- Performance Requirements: Factors such as handling, ride comfort, and load-carrying capacity influence suspension choices.
- Cost and Complexity: More sophisticated suspension systems often come with higher costs and maintenance requirements.
- Manufacturing Constraints: Vehicle platform sharing and production efficiencies can influence suspension design choices.

Advancements in Suspension Technology
Modern suspension systems have seen significant advancements in recent years:
- Active Suspension: These systems use electronic controls to adjust suspension characteristics in real-time, optimizing performance and comfort.
- Adaptive Damping: Electronically controlled shock absorbers can adjust their damping rates based on road conditions and driving style.
- Air Suspension: Using compressed air instead of traditional springs, these systems offer adjustable ride height and improved comfort.
- Magnetorheological Dampers: These advanced shock absorbers use magnetic fields to instantly adjust damping characteristics.
- Lightweight Materials: The use of materials like aluminum and carbon fiber in suspension components reduces unsprung weight, improving performance and efficiency.
Maintenance and Care of Suspension Systems
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of your vehicle’s suspension system:
- Regular Inspections: Visually inspect suspension components for signs of wear, damage, or leaks.
- Shock Absorber and Strut Replacement: Replace these components when they show signs of wear or typically every 50,000 to 100,000 miles.
- Wheel Alignment: Regular wheel alignments help prevent uneven tire wear and ensure optimal handling.
- Lubrication: Keep ball joints and other moving parts properly lubricated as per manufacturer recommendations.
- Tire Maintenance: Proper tire inflation and regular rotation contribute to overall suspension performance.
The Impact of Suspension on Vehicle Dynamics
A well-designed and properly maintained suspension system significantly influences various aspects of vehicle dynamics:
- Ride Quality: A good suspension system absorbs road imperfections, providing a smooth and comfortable ride for passengers.
- Handling: Proper suspension tuning ensures responsive steering and optimal tire contact with the road, enhancing overall vehicle control.
- Braking Performance: By maintaining consistent tire contact with the road surface, suspension systems contribute to shorter stopping distances and improved braking stability.
- Acceleration: Effective weight transfer management during acceleration improves traction and overall performance.
- Cornering Ability: Well-tuned suspension systems reduce body roll and maintain tire contact during cornering, enhancing stability and grip.
Choosing the Right Suspension for Your Vehicle
When considering suspension upgrades or replacements, keep the following factors in mind:
- Intended Use: Consider whether you prioritize comfort, performance, or a balance of both.
- Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure any aftermarket suspension components are compatible with your specific vehicle make and model.
- Budget: Balance your desired performance improvements with your budget constraints.
- Legal Considerations: Be aware of local regulations regarding vehicle modifications, especially concerning ride height and suspension alterations.
- Professional Installation: For complex suspension modifications, consider professional installation to ensure proper setup and alignment.

Conclusion
The suspension system is a critical component of any automobile, significantly influencing its performance, safety, and comfort. By understanding the various types, components, and functions of suspension systems, drivers can make informed decisions about vehicle maintenance and potential upgrades. As automotive technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovations in suspension design, leading to even safer, more comfortable, and better-performing vehicles in the future.
Remember, a well-maintained suspension system not only enhances your driving experience but also contributes to the longevity of your vehicle. Regular inspections and timely maintenance can help ensure your car’s suspension continues to perform optimally for years to come.