Introduction
Idling devices in carburetor systems play a crucial role in preventing engine stalling and ensuring smooth operation. However, with the increasing complexity of modern engines, the need for efficient anti-dieseling devices has become more pressing than ever. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of idling devices, exploring their functions, types, and applications. We will also discuss the latest anti-dieseling technologies and provide actionable insights to help you optimize your carburetor system.
What are Idling Devices in Carburetor Systems?
Idling devices, also known as idle circuits or idle mixture devices, are designed to provide a rich fuel mixture to the engine when it is idling. This ensures that the engine runs smoothly and efficiently, even at low speeds. Idling devices are typically used in carburetor systems, which are still widely used in many vehicles, especially in the automotive aftermarket.
What is a Carburetor?
A carburetor is a device that mixes air and fuel in the proper ratio for combustion in an internal combustion engine. It controls the engine’s air-fuel mixture across various operating conditions, including idling, acceleration, and cruising.
The Importance of Idling Devices
Idling devices in carburetors are responsible for maintaining a steady engine speed when the vehicle is not in motion. They ensure that the engine receives the correct amount of fuel-air mixture to keep running smoothly without stalling.
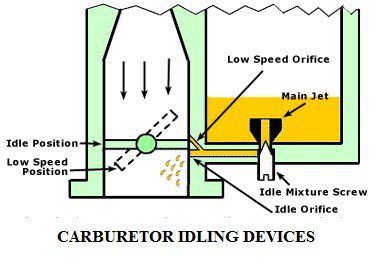
During idling, the throttle plate is almost in the closed position. Then the mass rate of air flow through the venture is small. Hence, the vacuum or depression produced at the venture is also small. With this small depression, no fuel can issue from the fuel orifice. Hence, an idling device is incorporated in the carburetor unit.
The engine idling devices can be seen in the picture. This device utilizes the large vacuum that prevails at the edge of the throttle plate for effecting fuel supply, when the throttle plate is almost in the closed position. The required idling mixture strength can be obtained by adjusting the idling air screw. The quantity of the mixture supplied to the engine is controlled by the throttle plate setting. This setting decides the extent of closure of the inlet passage by the throttle plate.
The idling devices operates at maximum capacity when the throttle plate is almost in the closed position. The effectiveness of the idling device gradually diminishes, as the throttle plate is being opened. When the throttle plate is wide open, the depression felt at the idling get is extremely small. This small depression is not capable of raising the fuel through the large height in the idling jet upto the discharge point. Now the maximum depression shifts to the venture throat. As such the main orifice starts supplying the fuel.
Components of Idling Devices
- Idle jet
- Idle mixture screw
- Idle speed screw
- Idle air passage
These components work together to regulate the fuel-air mixture and engine speed during idle conditions.
Types of Idling Devices
There are several types of idling devices available, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types include:
- Idle Mixture Screws: These screws adjust the air-fuel mixture when the engine is idling, ensuring a smooth and efficient operation.
- Idle Jets: Idle jets are small nozzles that supply fuel to the engine when it is idling. They are typically used in conjunction with idle mixture screws.
- Anti-Dieseling Valves: These valves prevent the engine from stalling by providing a rich fuel mixture when the engine is idling.
How Do Idling Devices Work?
Idling devices work by providing a rich fuel mixture to the engine when it is idling. This is achieved by adjusting the air-fuel ratio, which ensures that the engine runs smoothly and efficiently. The idling device monitors the engine’s speed and load, adjusting the fuel mixture accordingly.
Benefits of Idling Devices
Idling devices offer several benefits, including:
- Improved Engine Performance: Idling devices ensure that the engine runs smoothly and efficiently, even at low speeds.
- Reduced Engine Stalling: Idling devices prevent engine stalling, which can be a major safety concern.
- Increased Fuel Efficiency: Idling devices optimize the air-fuel mixture, resulting in improved fuel efficiency.
Common Issues with Idling Devices
Despite their benefits, idling devices can be prone to certain issues, including:
- Clogged Idle Jets: Clogged idle jets can prevent the engine from running smoothly, leading to stalling and poor performance.
- Worn-Out Idle Mixture Screws: Worn-out idle mixture screws can affect the air-fuel mixture, leading to poor engine performance.
- Faulty Anti-Dieseling Valves: Faulty anti-dieseling valves can prevent the engine from running smoothly, leading to stalling and poor performance.
Optimizing Idling Devices for Better Performance
To optimize idling devices for better performance, it is essential to:
- Regularly Clean and Maintain Idle Jets: Regular cleaning and maintenance of idle jets can prevent clogging and ensure smooth engine operation.
- Adjust Idle Mixture Screws: Adjusting idle mixture screws can ensure the optimal air-fuel mixture, resulting in improved engine performance.
- Replace Faulty Anti-Dieseling Valves: Replacing faulty anti-dieseling valves can prevent engine stalling and ensure smooth operation.
The Challenge of Dieseling
What is Dieseling?
Dieseling, also known as run-on or after-run, is a phenomenon where an engine continues to run after the ignition has been turned off. This occurs when there’s enough heat in the combustion chamber to ignite the fuel-air mixture without a spark.
Causes of Dieseling
- High engine operating temperature
- Carbon deposits in the combustion chamber
- Incorrect ignition timing
- Poor quality fuel
- Malfunctioning ignition switch
Anti-Dieseling Technology
The Role of Anti-Dieseling Devices
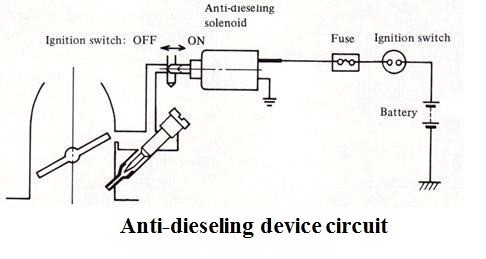
Anti-dieseling devices are designed to prevent the engine from continuing to run after the ignition is turned off. They work by cutting off the fuel supply to the engine when the ignition is switched off. A spark ignition engine sometime continues to run for a very small period, even after the ignition is switched off. This phenomena is called dieseling or after running. This causes wastage of fuel and pollution.
Some modern cars have the anti-dieseling system as shown in the picture. This system has a solenoid valve operated idling circuit. When the ignition switch is turned on, current flows in the coil of the solenoid valve and thereby generates a force. This force pulls a needle valve and opens the passage for slow speed mixture. When the ignition switch is turned off, the magnetic force disappears. Then the needle valve goes to the original position immediately by the action of the spring in the solenoid valve. By this way, the slow speed mixture passage is cut off. Hence, the engine stops and the fuel wastage are also eliminated.
Hot idling compensator: Some modern cars have this system in the carburetor unit. Under certain extremely hot operating conditions there is a tendency for the idling mixture to become too rich. This causes idling instability. The hot idling compensator system incorporates a bimetallic value which admits air directly into the manifold in correct quantity when needed. Thus the mixture richness is adjusted and stable idling is ensured.
Types of Anti-Dieseling Devices
- Solenoid-operated shut-off valves
- Mechanical shut-off valves
- Electric fuel pumps with built-in shut-off mechanisms
How Anti-Dieseling Devices Work
When the ignition is turned off, the anti-dieseling device is activated, either electrically or mechanically. This activation closes the fuel passage, preventing any additional fuel from entering the engine. Without fuel, the engine cannot continue running, effectively stopping the dieseling process.
Benefits of Anti-Dieseling Technology
- Improved engine longevity
- Enhanced fuel efficiency
- Reduced emissions
- Smoother engine operation
Optimizing Carburetor Performance
Maintaining Your Carburetor and Idling Devices
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring optimal performance of your carburetor and its idling devices. Here are some key steps:
- Clean the carburetor regularly
- Adjust the idle mixture screw
- Check and replace the idle jet if necessary
- Inspect and clean the idle air passage
Troubleshooting Common Idling Issues
If you’re experiencing problems with your engine’s idle, consider these potential causes:
- Clogged idle jet
- Incorrect idle mixture adjustment
- Vacuum leaks
- Worn throttle shaft bushings
When to Seek Professional Help
While many carburetor issues can be addressed through DIY maintenance, some problems may require professional attention. Consult a qualified mechanic, if you encounter:
- Persistent dieseling despite anti-dieseling device
- Severe engine misfires
- Significant loss of power
- Excessive fuel consumption
Conclusion
Idling devices play a critical role in ensuring smooth engine operation and preventing stalling. By understanding the different types of idling devices, their functions, and applications, you can optimize your carburetor system for better performance. Remember to regularly clean and maintain idle jets, adjust idle mixture screws, and replace faulty anti-dieseling valves to ensure optimal engine performance.