Spring suspension systems play a crucial role in the automotive industry, providing comfort, stability, and safety to vehicles of all types. This comprehensive guide delves into the two primary types of spring suspension systems: leaf springs and coil springs. We’ll explore their designs, applications, advantages, and disadvantages, as well as recent innovations in the field.
Understanding Spring Suspension Systems
The Importance of Suspension in Vehicles
Suspension systems are fundamental components in vehicles, serving several critical functions:
- Absorbing shocks and vibrations from road irregularities
- Maintaining proper tire contact with the road surface
- Supporting the vehicle’s weight
- Enhancing overall ride comfort and handling
A well-designed suspension system contributes significantly to a vehicle’s performance, safety, and longevity.
Basic Principles of Spring Suspension
Spring suspension systems operate on the principle of energy absorption and dissipation. When a vehicle encounters bumps or uneven terrain, the springs compress, storing potential energy. This energy is then released gradually, allowing the vehicle to maintain stability and comfort.
Introduction To Leaf Springs
Leaf spring a type of spring suspension system in automobile also denoted to as semi-elliptical springs are one of the ancient form of suspension used in vehicles, particularly heavy vehicles. A leaf spring appears like a bow minus the string. It contains of a stack of curved narrow plates of the same width and varied length clamped together with shorter plates at the center to form a semi-elliptical shape. The center of the arc delivers location for the axle, tie holes are made available at either end for getting attached to the body.
Leaf Spring Suspension System
Any spring, maybe it’s a leaf, torsion or coil spring, must compensate for irregularities in the road surface, keep the suspension system at a fixed height and support added weight without excessive sagging. Each of those works is very significant in providing comfort, specific handling and load-bearing ability in the modern vehicle – three key areas that will raise customer concerns.
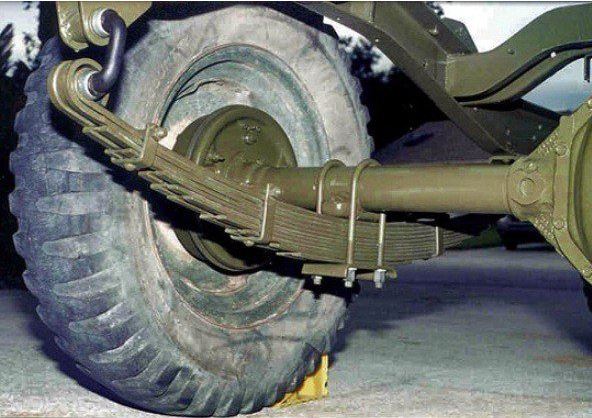

In ancient times the steel multi-leaf spring is one of the first-born and most widely used spring designs in suspension systems. The leaf spring have many advantages, not only it acts as a spring, but also because it attaches the axle straight to the chassis.
Types of Leaf Springs
There are two varieties of leaf springs. They are the mono-leaf springs and the multi-leaf springs. As the name proposes, the mono-leaf suspension involves of a single link. They are thick in the middle and narrowing out at the end. It does not offer much strength and suspension to dragged vehicles.

Multi-leaf springs are mainly used for heavier vehicles which offer increased strength and suspension. The recent development in design is the parabolic leaf spring. It can contain a mono-leaf or multi-leaf configuration. It has less leaves in comparison to the semi-elliptical multi-leaf springs whose thickness differs from center to the end and it follows a parabolic path. This shape not only saves weight but also provides greater flexibility which improves ride quality. A trade-off of using parabolic leaf spring is reduced load carrying capability.

Design and Construction
Leaf springs, also known as laminated springs, consist of several layers of curved metal strips called leaves. These leaves are stacked and bound together, forming an arc-shaped structure.
Components of a Leaf Spring:
- Master leaf: The longest and topmost leaf
- Graduated leaves: Progressively shorter leaves stacked beneath the master leaf
- Rebound clips: Metal clips that hold the leaves together
- Center bolt: Secures the leaves and attaches the spring to the axle
- Spring eyes: Curved ends of the master leaf for mounting
Applications
Leaf springs are commonly used in:
- Heavy-duty vehicles (trucks, buses)
- Commercial vehicles
- Off-road vehicles
- Some passenger cars (particularly in rear suspensions)
Advantages of Leaf Springs
- High load-bearing capacity
- Simplicity in design and manufacturing
- Cost-effectiveness
- Durability and longevity
- Ability to distribute weight evenly
Disadvantages of Leaf Springs
- Increased weight compared to coil springs
- Limited flexibility in suspension tuning
- Potential for inter-leaf friction and noise
- Less responsive to small bumps and vibrations
Recent Innovations in Leaf Spring Technology
- Composite leaf springs: Made from materials like fiberglass or carbon fiber, offering weight reduction and improved performance
- Parabolic leaf springs: Featuring a parabolic taper for better ride quality and reduced weight
- Air-assisted leaf springs: Combining traditional leaf springs with air springs for adjustable ride height and improved load-carrying capacity
Coil Spring Suspension System
The function of a coil spring can be well understood if we imagine it as a long, thin, torsion bar twisted into a coil shape. Because the coiled wire twists through the spring’s compression/extension cycles, the coil spring essentially functions on the same principle as a torsion bar.
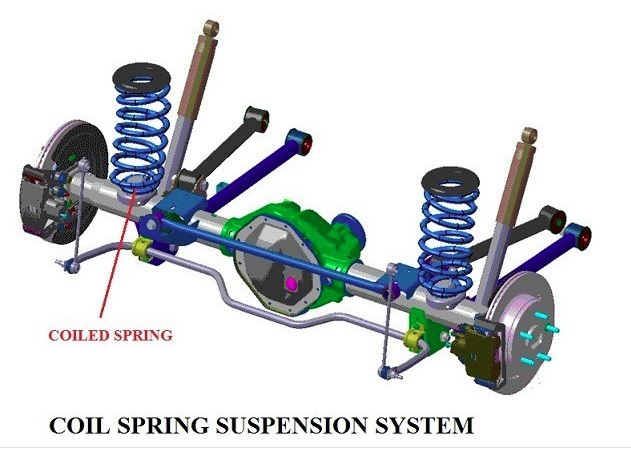
As a coil spring occupies a relatively small space, it can be used in a most types of suspension designs including MacPherson strut, solid axle with trailing arms, independently sprung rear axle, or any SLA suspension system using a spring or coil-over shock absorber configuration.
Most recent imports use the coil spring in differences of the MacPherson strut design. In common, wire gauge, length, overall diameter and numbers of coils control the characteristics of the coil spring.
Sometimes a coil spring can be considered as a variable rate spring that increases load-bearing capability as it’s compressed. Flexible rate coil springs are often used in chassis configurations that rarely carry heavy loads.
Design and Construction
Coil springs, also called helical springs, are made from a single piece of spring steel wound into a spiral shape.
Components of a Coil Spring System:
- Spring coil: The main body of the spring
- End coils: Flattened ends for mounting
- Spring seats: Platforms that hold the spring in place
- Dampers (shock absorbers): Work in conjunction with the springs to control oscillation
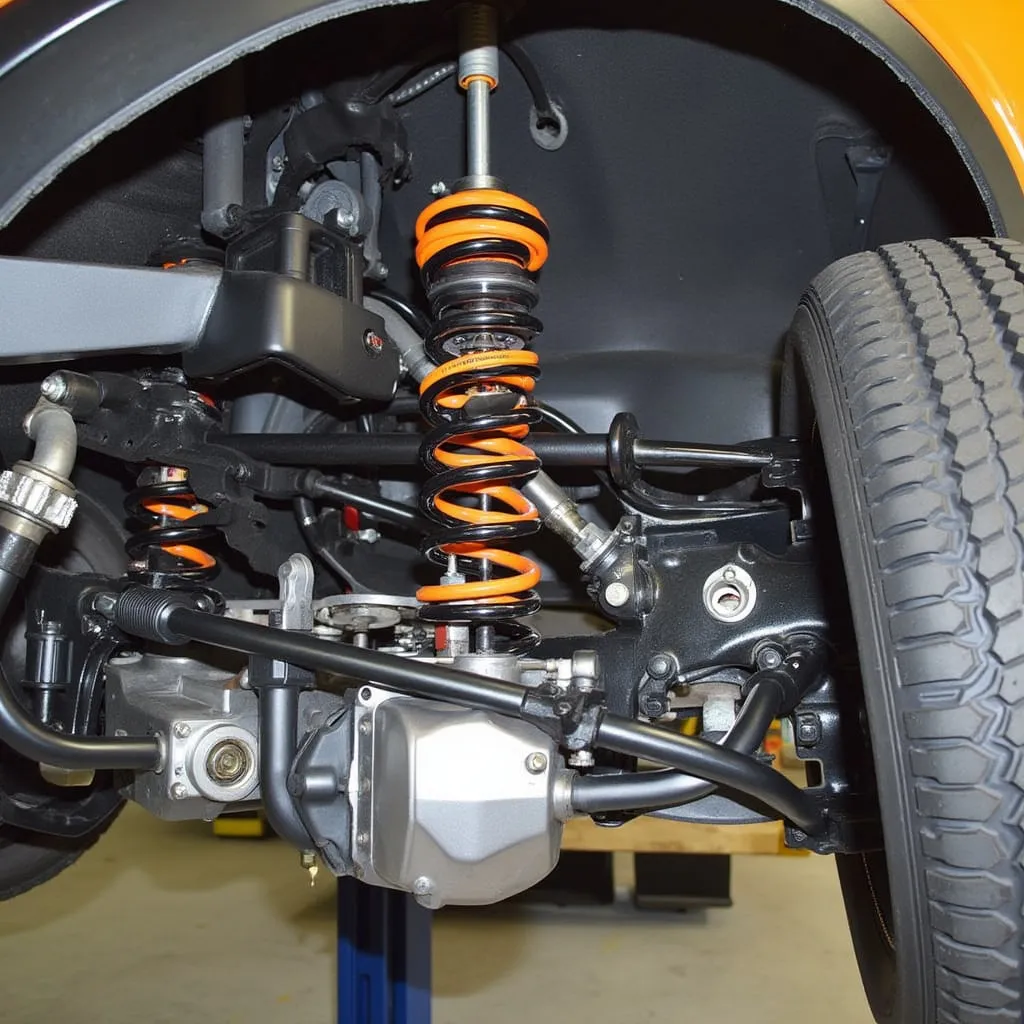

Applications
Coil springs are widely used in:
- Passenger cars
- Light trucks and SUVs
- Motorcycles
- Some heavy-duty vehicles (in combination with other suspension types)
Advantages of Coil Springs
- Excellent ride comfort and handling
- Compact design, allowing for more flexible vehicle layouts
- Wide range of spring rates available
- Minimal friction during operation
- Easy to replace and maintain
Disadvantages of Coil Springs
- Lower load-bearing capacity compared to leaf springs
- Potential for side-load issues if not properly designed
- May require additional components for axle location
Innovations in Coil Spring Technology
- Variable rate springs: Offer progressive spring rates for improved ride quality
- Air-assisted coil springs: Combine traditional coil springs with air springs for adjustable ride height and improved load-carrying capacity
- Magnetic ride control: Uses magnetorheological fluid-filled dampers to adjust suspension characteristics in real-time
Comparing Leaf Springs and Coil Springs
Performance Characteristics
- Ride Comfort:
- Coil springs generally provide better ride comfort due to their ability to respond quickly to small bumps and vibrations.
- Leaf springs offer a firmer ride, which can be advantageous for heavy loads but may compromise comfort in passenger vehicles.
- Handling:
- Coil springs typically offer better handling characteristics, allowing for more precise suspension tuning.
- Leaf springs provide stability and are well-suited for heavy-duty applications but may result in less responsive handling in passenger vehicles.
- Load Capacity:
- Leaf springs excel in load-bearing capacity, making them ideal for heavy-duty vehicles and commercial applications.
- Coil springs have limitations in load capacity but can be designed to handle moderate loads effectively.
- Durability:
- Both leaf springs and coil springs can be highly durable when properly designed and maintained.
- Leaf springs may have an edge in extreme conditions due to their simpler construction.
Choosing the Right Spring Suspension System
Selecting the appropriate spring suspension system depends on various factors:
- Vehicle type and intended use
- Load-carrying requirements
- Desired ride quality and handling characteristics
- Cost constraints
- Maintenance considerations
- Regulatory requirements (e.g., for commercial vehicles)
For passenger vehicles prioritizing comfort and handling, coil springs are often the preferred choice. Heavy-duty and commercial vehicles that require high load-bearing capacity typically benefit from leaf spring systems.
Advantages of Spring Suspension System
- 1) The manufacture of the suspension is simple and strong as it performances as a linkage for holding the axle in place and thus a separate linkage isn’t necessary.
- 2) As they detect the rear axle, the need for trailing arms and panhard rod is removed, thus saving cost and weight.
- 3) It provisions the weight of the chassis.
- 4) It controls chassis roll more proficiently by utilizing a higher rear moment center and a wider spring base.
Disadvantages of Spring Suspension System
- 1) The leaf-spring systems are difficult to install.
- 2) The inter-leaf friction between the leaf springs decreases the ride comfort.
- 3) The leaf springs may be apt to to lose shape and sag over time.
- 4) Acceleration and braking torque roots wind-up and vibration. Also wind-up causes rear-end squat and nose-diving.
Conclusion
Spring suspension systems, whether leaf springs or coil springs, play a vital role in vehicle performance, safety, and comfort. Understanding the characteristics, advantages, and limitations of each type allows for informed decision-making in vehicle design and maintenance. As automotive technology continues to evolve, we can expect further innovations in spring suspension systems, leading to improved vehicle dynamics, efficiency, and sustainability.